Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is essential for overall health and well-being. Whether aiming to prevent diabetes, manage an existing condition, or boost your energy levels, understanding the nuances of blood sugar is key. Unfortunately, misconceptions and myths often cloud the topic, making it harder to separate fact from fiction. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore blood sugar, why it matters, and how to manage it effectively through diet, lifestyle, and natural remedies.
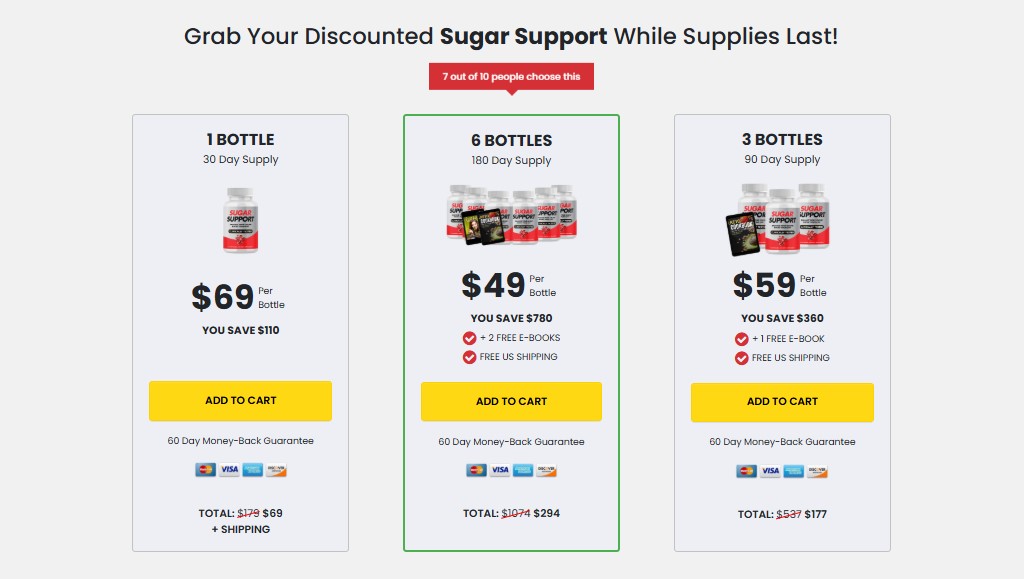
What is Sugar Support?
Sugar Support, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for your body’s cells. It comes from the foods you eat, particularly carbohydrates, and is transported through your bloodstream to cells where it’s used for energy. A hormone called insulin, produced by the pancreas, helps regulate this process. For most individuals, normal blood sugar levels range between 70–99 mg/dL when fasting and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. Consistently high or low levels can signal underlying health issues.
Why is Blood Sugar Important?
Stable blood sugar levels ensure that your body functions optimally. High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can lead to complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and heart problems, while low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can cause dizziness, confusion, and fainting. Proper blood sugar management also helps maintain energy levels, mental clarity, and physical performance. Whether you’re working out or working hard, balanced glucose keeps you on your game.
What Is Blood Sugar and Why Is It Important?
Blood sugar, or glucose, is a crucial energy source for your body. It comes from the food you eat, primarily carbohydrates, and fuels your brain, muscles, and organs. However, too much or too little can cause serious health issues.
Normal Blood Sugar Range: A healthy fasting blood sugar range is typically between 70–99 mg/dL.
Why It Matters: Imbalanced blood sugar can lead to conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and chronic fatigue.
How Blood Sugar Affects the Body
Your body works hard to maintain blood sugar levels within a tight range. The pancreas releases insulin to lower blood sugar and glucagon to raise it when needed. Here’s what happens when it’s not balanced:
High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia): Damages nerves, blood vessels, and organs over time.
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia): Leads to dizziness, confusion, and potential loss of consciousness.
Common Causes of Blood Sugar Imbalance
Understanding what disrupts your blood sugar is key to preventing issues. Some common culprits include:
Poor Diet: High-sugar, low-fiber diets spike glucose levels.
Lack of Exercise: Physical inactivity reduces insulin sensitivity.
Chronic Stress: Stress hormones like cortisol can increase blood sugar.
Inadequate Sleep: Poor sleep disrupts insulin regulation.
Underlying Health Conditions: Thyroid disorders and diabetes affect blood sugar.
Symptoms of High and Low Blood Sugar
- High Blood Sugar Symptoms
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Fatigue and blurry vision
- Slow wound healing
- Unexplained weight loss
Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
- Shakiness and sweating
- Sudden hunger
- Irritability or confusion
- Rapid heartbeat
Spotting these symptoms early can prevent complications. If you’re unsure, consult with a healthcare provider.
Dietary Tips for Blood Sugar Support
Foods That Stabilize Blood Sugar
Incorporate these into your meals:
High-Fiber Foods: Oats, legumes, and vegetables
Healthy Fats: Avocado, nuts, and seeds
Lean Proteins: Fish, chicken, tofu
Foods to Avoid for Better Control
Limit these:
- Sugary beverages and snacks
- Refined carbs like white bread and pasta
- Trans fats and processed foods
- Pairing proteins with carbs and eating small, frequent meals can also help stabilize blood sugar.
The Role of Exercise in Blood Sugar Balance
Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and lowers blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly. Popular activities include:
Walking: A simple way to lower post-meal glucose spikes.
Strength Training: Builds muscle, which uses glucose more efficiently.
Yoga: Reduces stress, which can affect blood sugar.
Natural Supplements for Sugar Support
Many supplements can aid blood sugar management. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting. Popular options include:
Cinnamon: May improve insulin sensitivity.
Chromium: Helps metabolize glucose.
Magnesium: Supports insulin action.
Berberine: Known for reducing glucose levels.
The Importance of Sleep and Stress Management
Chronic stress and sleep deprivation wreak havoc on blood sugar levels. Here’s what you can do:
Stress Management: Practice meditation, deep breathing, or hobbies.
Improving Sleep: Stick to a regular schedule, and reduce screen time before bed.
FAQs on Blood Sugar Support
What is the best way to quickly lower blood sugar?
Drink water and go for a walk to help reduce levels.
Can I reverse prediabetes naturally?
Yes, through diet, exercise, and weight loss.
Which foods are worst for blood sugar?
Sugary drinks, refined carbs, and processed snacks are the worst offenders.
How does stress affect blood sugar?
Stress increases cortisol, which raises blood sugar levels.
Are sugar substitutes safe for managing blood sugar?
Some, like stevia and erythritol, are safe; others, like aspartame, may have side effects.